GERMAN PRIETO
Research
My main interest is to use seismic records to understand the earthquake source, the interior of the Earth and how both affect the ground motions that we feel on the Earth’s surface. Seismological observations are affected by the internal structure of the Earth, for example amplification of seismic waves in sedimentary basins. The nature of the earthquake source has also a significant impact on ground motions, and I am interested in a better understanding of earthquake ruptures, i.e., are large earthquakes different from the more common small ones? How are deep earthquakes different from shallower ones?
Ambient Seismic Noise
Error Analysis
Intermediate-Depth and Deep Earthquakes
Research
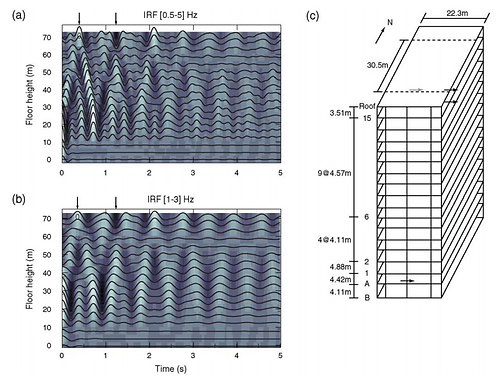
Earthquake Engineering and Health Monitoring
Earthquake Source Physics
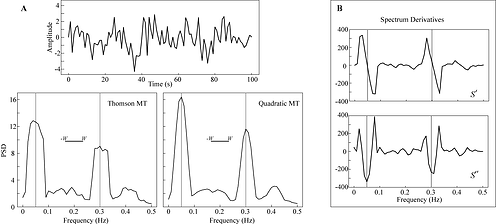
Spectrum Estimation Methods
german prieto
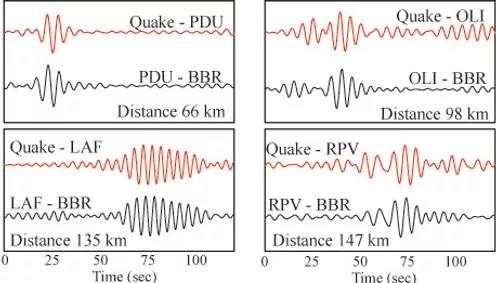
Ambient Seismic Noise
The signal that is sometimes regarded as noise, the ambient seismic field, has recently been shown to provide important information about Earth’s structure. Surface wave tomography, body wave tomography both for crustal and deep interfases, crustal anysotropy, attenuation tomography and basin amplification have all been studied using these signals. By looking at the spatially coherent signals between seismic stations (and under certain conditions) we are able to extract the impulse
response record that is quite similar to the Green’s function of the medium, as if one station behaved like a source and the others record the response of the Eartth’s crust and upper mantle. In my research I have been focusing in additional information observed in the amplitudes of these empirical Green’s functions, both in time and frequency domains
german prieto
Intermediate-Depth and Deep Earthquakes
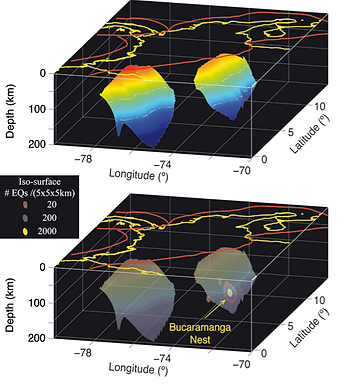
The physical mechanism responsible for intermediate-depth earthquakes is still under debate. In contrast to conditions in the crust and shallow lithosphere, at temperatures and pressures corresponding to depths >50 km one would expect rocks to yield by creep or flow and not by brittle failure. Earthquake nests represent a region with high earthquake concentration that is isolated from nearby activity, and one such regions is the intermediate-depth Bucaramanga Nest. Given the nature and characteristics of this nest, it can be thought as natural laboratories for understanding the mechanism of intermediate-depth earthquakes. I am studying this place using a wide variety of seismological tools to resolve this issue.
german prieto
Earthquake Source Physics
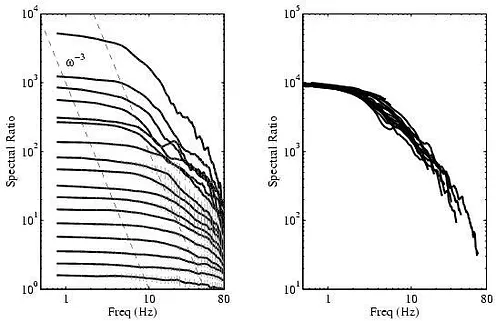
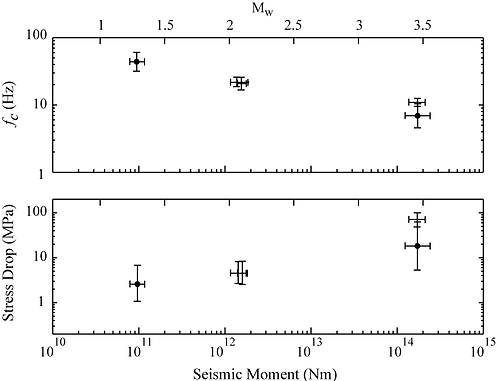
A major question in seismology is whether the earthquake process is self-similar. Is a M = 8.0 earthquake simply a M = 2.0 earthquake scaled by a large factor or is the physics of the two processes different? There is continuing interest in the question of earthquake scaling and there is currently a debate regarding the self-similarity of the earthquake rupture over their entire size range. Seismologists use some parameters (such as seismic moment, stress drop, and radiated seismic energy) to describe the earthquake rupture. The behavior of some of this parameters
as a function of the earthquake size provides information about the physics of the rupture process
german prieto
Error Analysis
Part of the difficulty in studying earthquake source scaling is the accurate estimation of the source parameters, accounting for seismic attenuation, path effects, etc. These factors lead to considerable uncertainties in the estimation of stress drop or radiated seismic energy. What is often missing in many studies is these measurements of uncertainty, which are of key importance when comparing two results, or when comparing different methods of analysis.
german prieto
Spectrum Estimation Methods
The are multiple applications in geophysics (e.g., seismology, climate, electromagnetics), engineering (e.g., structural engeneering), medicine, and even the social sciences (e.g., economics) where relevant information may be extracted from the frequency content of the spectrum.
In 1982 David J. Thomson introduced the multitaper spectrum algorithm which has been widely used since. In my analysis of
the earthquakes I have used the multitaper method extensively. I wrote a Fortran 90/95 Library (mwlib.html) with many more features than other available codes. The algorithm allows for the estimation of the power spectra of a signal, confidence intervals, phase information, correlations, coherency, deconvolution, etc..
german prieto
Earthquake Engineering and Health Monitoring
The linear impulse response of an engineering structure (building, bridge, etc) can be used for structual health monitoring (SHM), and potential detecting damage and the location of the damage inside the structure. The impulse response of the building can be estimated using ambient vibrations recorded by seismic sensors inside the structure.
We are developing new tools using seismic interferometry for SHM, using data from various buildings and state-of-the-art signal processing methods that will hopefully provide new ways for continuous monitoring and damage detection.